From this analysis, you can see that if you can reduce the cost variables, you can lower your breakeven point without having to raise your price. At that breakeven price, the homeowner would exactly break even, neither making nor losing any money. If you find yourself asking these questions, it’s time to perform break-even analysis. Read on to learn all about how break-even analysis can serve your small business. Check out some examples of calculating your break-even point in units.
Outsource fixed costs
This will give us the total dollar amount in sales that will we need to achieve in order to have zero loss and zero profit. Now we can take this concept a step further and compute the total number of units that need to be sold in order to achieve a certain level profitability with out break-even calculator. Calculating breakeven points can be used when talking about a business or with traders in the market when they consider recouping losses or some applied overhead vs actual overhead initial outlay. Options traders also use the technique to figure out what price level the underlying price must be for a trade so that it expires in the money. A breakeven point calculation is often done by also including the costs of any fees, commissions, taxes, and in some cases, the effects of inflation. Finally, the breakeven analysis often ignores qualitative factors such as market competition, customer satisfaction, and product quality.
Methods to Calculate Break-Even Point
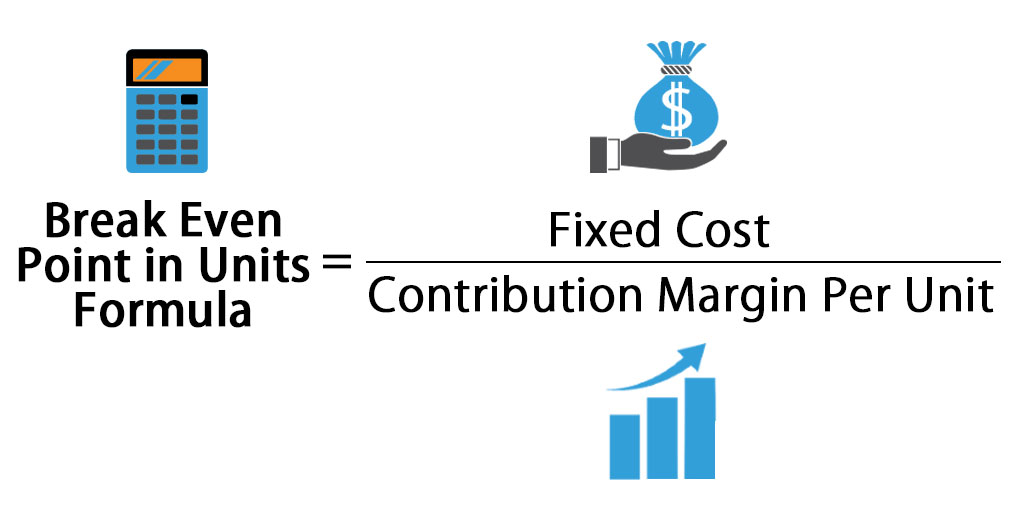
For instance, if management decided to increase the sales price of the couches in our example by $50, it would have a drastic impact on the number of units required to sell before profitability. They can also change the variable costs for each unit by adding more automation to the production process. Lower variable costs equate to greater profits per unit and reduce the total number that must be produced. The break-even point formula is calculated by dividing the total fixed costs of production by the price per unit less the variable costs to produce the product. It is also possible to calculate how many units need to be sold to cover the fixed costs, which will result in the company breaking even. To do this, calculate the contribution margin, which is the sale price of the product less variable costs.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?

Finding your break-even point gives you a better idea of which risks are really worth taking. To find your break-even point, divide your fixed costs by your contribution margin ratio. This gives you the number of units you need to sell to cover your costs per month.
- Please go ahead and use the calculator, we hope it’s fairly straightforward.
- Now we can take this concept a step further and compute the total number of units that need to be sold in order to achieve a certain level profitability with out break-even calculator.
- The break-even point (BEP) helps businesses with pricing decisions, sales forecasting, cost management, and growth strategies.
- A break-even analysis can help you see where you need to make adjustments with your pricing or expenses.
- It is only useful for determining whether a company is making a profit or not at a given point in time.
Break-even analysis is an important way to help calculate the risks involved in your endeavor and determine whether they’re worthwhile before you invest in the process. Even though break-even analysis can help forge a path to profitability, it’s not a perfect analytical tool. If you’d prefer to calculate how many units you need to sell before breaking even, you can use the number of units in your calculation. Break-even analysis, also known as break-even point analysis, involves calculating the point at which a business breaks even and what steps it might take to become profitable. A break-even analysis can help you see where you need to make adjustments with your pricing or expenses. This means Sam’s team needs to sell $2727 worth of Sam’s Silly Soda in that month, to break even.
Also, remember that this analysis doesn’t take into consideration the present vs. future value of your funds. See the time value of money calculator for more information about this topic. Changing industry regulations or compliance requirements might force you to change operations or invest in different technology or infrastructure.
The break-even point is your total fixed costs divided by the difference between the unit price and variable costs per unit. Keep in mind that fixed costs are the overall costs, and the sales price and variable costs are just per unit. In other words, the breakeven point is equal to the total fixed costs divided by the difference between the unit price and variable costs.
Finding the break-even point of your business allows you to determine how much more revenue you need to generate in order to reach a profit. Conversely, it can also help you determine how many costs you need to cut to reach profitability. Out of the several ways to measure your business’s profitability, calculating the break-even point is one of the most simplistic. On the other hand, variable costs change based on your sales activity. Examples of variable costs include direct materials and direct labor.
In corporate accounting, the breakeven point (BEP) is the moment a company’s operations stop being unprofitable and starts to earn a profit. The breakeven point is the production level at which total revenues for a product equal total expenses. The breakeven point can also be used in other ways across finance such as in trading. Break-even analysis can also be a great way to measure and benchmark your business’s performance over time.
The total variable costs will therefore be equal to the variable cost per unit of $10.00 multiplied by the number of units sold. In terms of its cost structure, the company has fixed costs (i.e., constant regardless of production volume) that amounts to $50k per year. Recall, fixed costs are independent of the sales volume for the given period, and include costs such as the monthly rent, the base employee salaries, and insurance.
Thus, if a project costs $1 million to undertake, it would need to generate $1 million in net profits before it breaks even. The breakeven point is important because it identifies the minimum sales volume needed to cover all costs, ensuring no losses are incurred. It aids in strategic decision-making regarding pricing, cost control, and sales targets.